| Browse | Text search | Protein search | Domain search | Download | User manual | Related links | Citation & Contact |
The Gram-negative porin 4 (GBP-4) Family [Function: Non-specific diffusion channels] Seed alignment | Full alignment | Pfam page | TC-DB page | ||||
General bacterial porins are a family of proteins from the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. The porins act as molecular filters for hydrophilic compounds. They are responsible for the 'molecular sieve' properties of the outer membrane. Porins form large water-filled channels which allow the diffusion of hydrophilic molecules into the periplasmic space. Some porins form general diffusion channels that allow any solutes up to a certain size (that size is known as the exclusion limit) to cross the membrane, while other porins are specific for one particular solute and contain a binding site for that solute inside the pores (these are known as selective porins). As porins are the major outer membrane proteins, they also serve as receptor sites for the binding of phages and bacteriocins. The outer membrane protein OmpU is the most abundant outer membrane protein in V. cholerae, and has been identified as an important virulence factor that is involved in host-cell interaction and recognition, as well as being critical for the survival of the pathogenic V. cholerae in the host body and in harsh environments. The crystal structure of the V. cholerae OmpU trimer is reported to a resolution of 2.2 Å. The protomer forms a 16-ß-stranded barrel with a noncanonical N-terminal coil located in the lumen of the barrel that consists of residues Gly32-Ser42 and is observed to participate in forming the second gate in the pore. | ||||
Representative image: 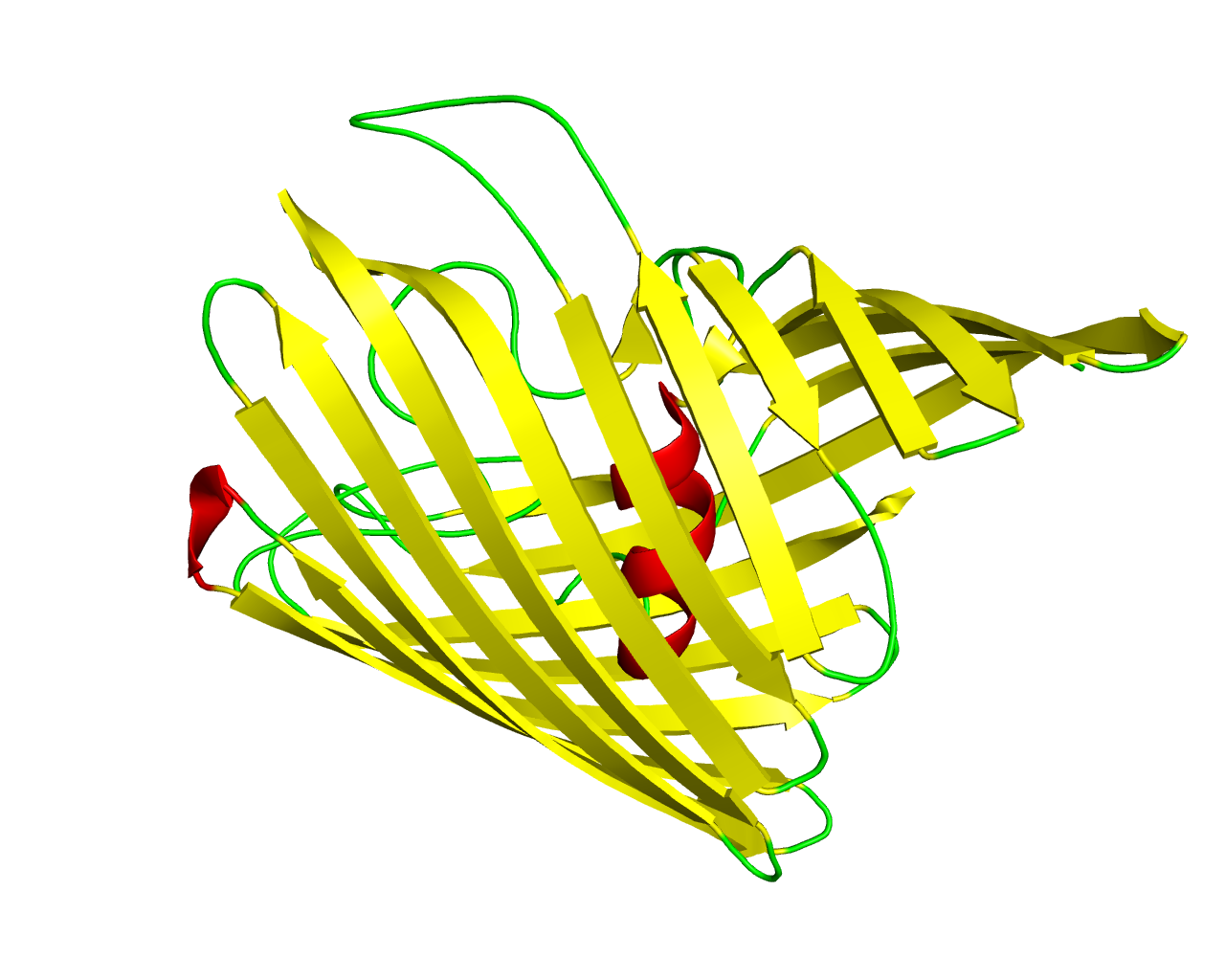 | ||||
| Literature references | ||||
Structural basis for chitin acquisition by marine Vibrio species Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 15;9(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02523-y. PMID: 29335469 | ||||
Crystal structure of the outer membrane protein OmpU from Vibrio cholerae at 2.2 Å resolution Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018 Jan 1;74(Pt 1):21-29. doi: 10.1107/S2059798317017697. Epub 2018 Jan 1. PMID: 29372896 | ||||
Maximized Autotransporter-Mediated Expression (MATE) for Surface Display and Secretion of Recombinant Proteins in Escherichia coli Food Technol Biotechnol. 2015 Sep;53(3):251-260. doi: 10.17113/ftb.53.03.15.3802. PMID: 27904356 | ||||
Amphipols outperform dodecylmaltoside micelles in stabilizing membrane protein structure in the gas phase Anal Chem. 2015 Jan 20;87(2):1118-26. doi: 10.1021/ac5037022. Epub 2014 Dec 30. PMID: 25495802 | ||||
Amphipathic polymers enable the study of functional membrane proteins in the gas phase Anal Chem. 2012 Nov 20;84(22):9841-7. doi: 10.1021/ac302223s. Epub 2012 Oct 29. PMID: 23072351 | ||||
Asymmetric conductivity of engineered porins Protein Eng. 2002 Oct;15(10):799-804. doi: 10.1093/protein/15.10.799. PMID: 12468713 | ||||
Structure of the membrane channel porin from Rhodopseudomonas blastica at 2.0 A resolution Protein Sci. 1994 Jan;3(1):58-63. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030108. PMID: 8142898 | ||||
Structure of porin refined at 1.8 A resolution J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):493-509. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90903-w. PMID: 1328651 | ||||
The bacterial porin superfamily: sequence alignment and structure prediction Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2153-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02145.x. PMID: 1662760 | ||||
Biophysics of the structure and function of porins Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Nov;23(4):367-403. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000559x. PMID: 2178269 | ||||
Permeation of hydrophilic molecules through the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Review on bacterial porins Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):1-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14245.x. PMID: 2901351 | ||||
| Proteins in this family with 3D-structure | ||||
View Entry | Description | Organism | Length | # strands |
